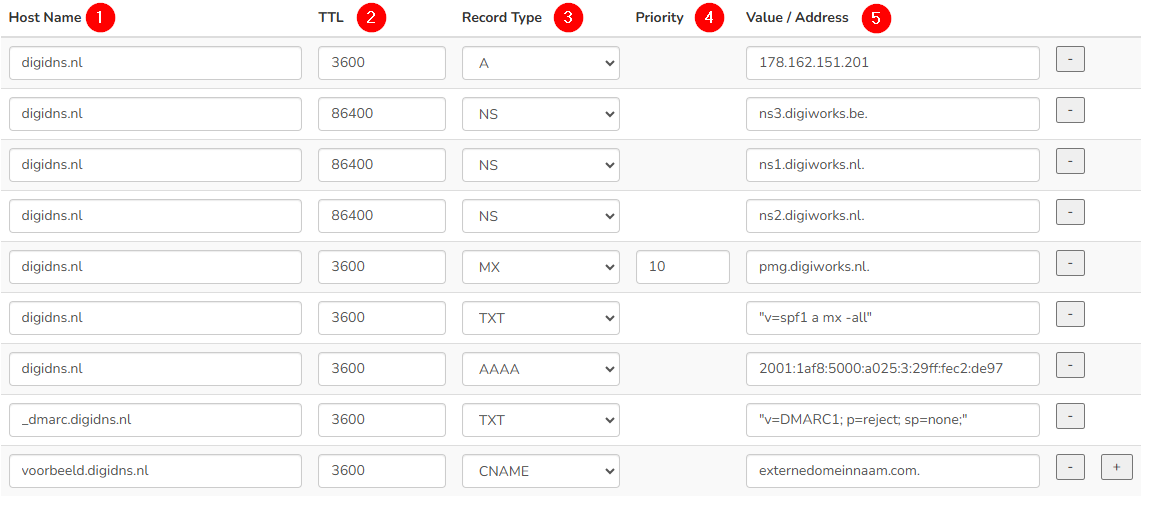
1. Hostname
"This is always the domain name or sub-domain name. If an @ appears in the examples from a service provider, enter the relevant domain name. No period ( . ) should be placed after the domain name in this field.
2. TTL (Time to Live)
TTL is a value that indicates how long a DNS record remains valid in the cache of a DNS server or a client. It is expressed in seconds. For us, these are usually set to 1 hour (3600) for A, AAAA, TXT, TLSA. NS records are set to 24 hours (86400).
3. Record Type
Different record types available, such as:
- A Record (Function: Connects a domain name to an IPv4 address.
Example: example.com -> 192.0.2.1) - AAAA Record (Function: Connects a domain name to an IPv6 address.
Example: example.com -> 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334) - CNAME Record (Function: Points a domain name to another domain name.
Example: www.example.com -> example.com.) - MX Record (Function: Specifies the mail servers responsible for receiving email for the domain.
Example: example.com -> mail.example.com.) - NS Record (Function: Specifies the name servers that have authority over the domain.
Example: example.com -> ns1.example.com.) - SRV Record (Function: Provides information about available services and their locations.
Example: _sip._tcp.example.com -> sipserver.example.com.) - TXT Record (Function: Stores text information for various purposes, such as verification and SPF (Sender Policy Framework).
Example: example.com -> "v=spf1 include:_spf.example.com -all") - TLSA Record (Function: Connects a TLS server certificate to a domain name, helping to secure communication.
Example: _443._tcp.example.com -> 3 1 1 9a5c4e5e6b5c4e5e6b5c4e5e6b5c4e5e6b5c4e5e6b5c4e5e6b5c4e5e6b5c4e5e)
4. Priority in MX-records (e-mail)
Each MX record has a priority value, also known as "preference" or "priority."
This value is an integer, where a lower value indicates a higher priority.
How does it work? When an email is sent to a domain, the sending mail server looks at the MX records of that domain.
The mail server first tries to contact the mail server with the highest priority (lowest number).
If the mail server with the highest priority is not available, the sending mail server tries the next mail server in the list, based on the priority values.
Example: Suppose a domain has the following MX records:
10 mail1.example.com
20 mail2.example.com
30 mail3.example.com
In this case, the sending mail server will first try to deliver the email to mail1.example.com.If this is not available, the mail server will try to deliver the email to mail2.example.com, and if that is also not available, to mail3.example.com.
The priority of MX records ensures that email is reliably delivered, even if one of the mail servers is not available.
Important! There should only be one priority value for MX records in the entire zone. If you have subdomains with an MX record in addition to your main MX, use a different priority value.
For example:
example.com > mailserver1.microsoft.com | Prio:10
example.com > mailserver2.microsoft.com | Prio:20
example.com > mailserver3.microsoft.com | Prio:30
subdomein.example.com > mailserver1.microsoft.com | Prio:11
subdomein.example.com > mailserver2.microsoft.com | Prio:21
subdomein.example.com > mailserver3.microsoft.com | Prio:31
5. Adres / Waarde / Value
The value in this field depends on the record type. Below are examples with the values as they should be entered::
A-record: Always an IP address, for example: 1.2.3.4
AAAA-record: Always an IPv6 address, for example: 2a0b:f380:3e8::24f
CNAME-record: Always a domain name (always end the domain name with a .), for example: server1.example.com.
MX-record: Always a domain name (always end the domain name with a .), for example: pmg.digiworks.nl.
TXT-record: This is variable text (the value must always be enclosed in "" quotes), for example: "v=spf1 include:_spf.example.com -all"
TLSA-record: See the display/explanation for non-daily records on the DNS Manager page
SRV-record: See the display/explanation for non-daily records on the DNS Manager page

